

The universe is supposed to be “running down” as a result of this.Įxplore zeroth law of thermodynamics Units of EntropyĮntropy changes ΔS= Tqrev (the change in the value of entropy is called entropy change). It depicts the maximum number of microscopic ways according to which the macroscopic state corresponding to S can be realized that is, S = k ln Ω, where k is the Boltzmann constant related to molecular energy.īecause all spontaneous processes are irreversible, the world’s entropy is said to be growing, meaning that more and more energy becomes unavailable for conversion into work. Entropy is a broad attribute whose quantity is determined by the amount of material in the system.įor an extensive system in thermodynamic equilibrium, entropy S is proportional to the natural logarithm of a quantity Ω. This equation describes the system as a thermodynamic state variable, meaning that its value is entirely determined by its present state rather than how it got there. As a result, it is possible to assert that The gas may, for example, be allowed to expand freely into a vacuum and do no work.
#UNITS OF ENTROPY PLUS#
Because when maximum work is done, the net entropy change for the system plus reservoir is zero, and the entropy of the reservoir falls by an amount dS reservoir = dQ/T, which is then counterbalanced by an increase of entropyįor the present working gas, so that dS system + dS reservoir = 0.īecause less than the maximum amount of work is done in any practical process (due to friction, for example), the actual quantity of heat dQ′ absorbed from the heat reservoir is less than the maximum dQ. As a result, dQ = dU + PdV due to energy conservation. As the gas expands, its internal energy may change by dU. When a gas absorbs a total quantity of heat dQ from a heat reservoir at temperature T and expands reversibly against the highest feasible restraining pressure P, the gas does the maximum work dW = P dV, where dV is the volume change. The entropy changes of the working substance in a heat engine, such as a gas in a cylinder with a moveable piston, may also be calculated using the same approach. The requirement ΔS = 0 corresponds to the minimum feasible value of Q2Īs the basic equation determining the efficiency of all heat engines, a slight modification would be enough to make the heat engine operate backward as a refrigerator a process with ΔS = 0 is reversible. However, Q2 cannot be 0 because this would break the second rule by making S negative. Q2 should be as tiny as feasible concerning Q1 to make W as large as possible. For the entire cycle, suppose a heat engine collects heat Q1 from R1 and exhausts heat Q2 to R2. The conditionΔ S= 0 establishes the highest attainable efficiency of heat engines, which are systems like gasoline or steam engines that may cyclically do work. T1 = T2 indicates that the reservoirs are in equilibrium, that no heat flows, and that ΔS = 0. As a result, the heat never flows spontaneously from cold to hot is comparable to a spontaneous flow of heat needing a positive net entropy change. Hence, the equation of entropy is hereunder: The net entropy change for the two reservoirs is if heat Q travels from R1 to R2. Assume at temperatures T1 and T2 there are two heat reservoirs R1 and R2 (such as the stove and the block of ice).
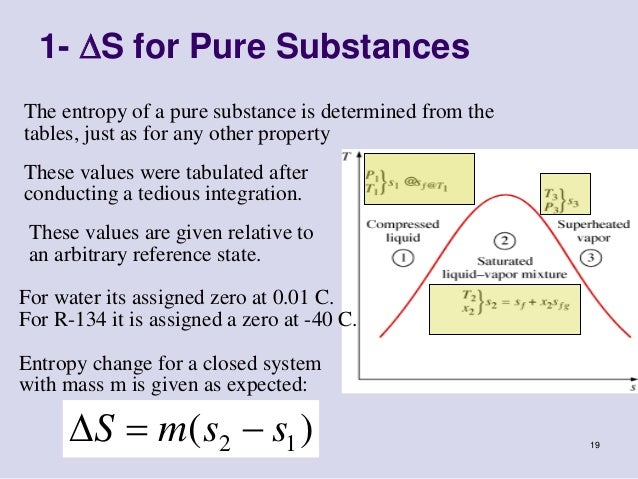
This equation essentially presents an alternate temperature definition that coincides with the standard definition. Formula or Equation of EntropyĪccording to the Clausius definition, if a quantity of heat Q flows into a huge heat reservoir at a temperature T above absolute zero, the entropy increase is S = Q/T. The system is in equilibrium with its surroundings for reversible processes but not for irreversible processes. Because a minor increase in the restraining force can switch the direction of the process from expansion to compression, the latter is reversible. Similarly, compressed gas confined in a cylinder might either expand freely into the atmosphere (an irreversible process) if a valve was opened, or it could accomplish beneficial work by moving a movable piston against the force required to confine the gas. It is reversible because just a minuscule amount of heat is required to reverse the process from progressive freezing to progressive thawing. In contrast, depending on whether a tiny amount of heat is given to or taken from the system, a block of ice placed in an ice-water bath will melt or freeze a bit more.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
